Life Cycle of Albugo Candida: Process & Mechanism with Zygotic Meiosis
Biology • June 15, 2025
Swaraj Barik
Introduction
The life cycle of Albugo candida, a fungal pathogen causing white rust, showcases a fascinating interplay of vegetative growth, rapid asexual multiplication, and robust sexual reproduction. This process is critical for understanding plant pathology, especially for protecting crops like mustard, cabbage, and other cruciferous vegetables.
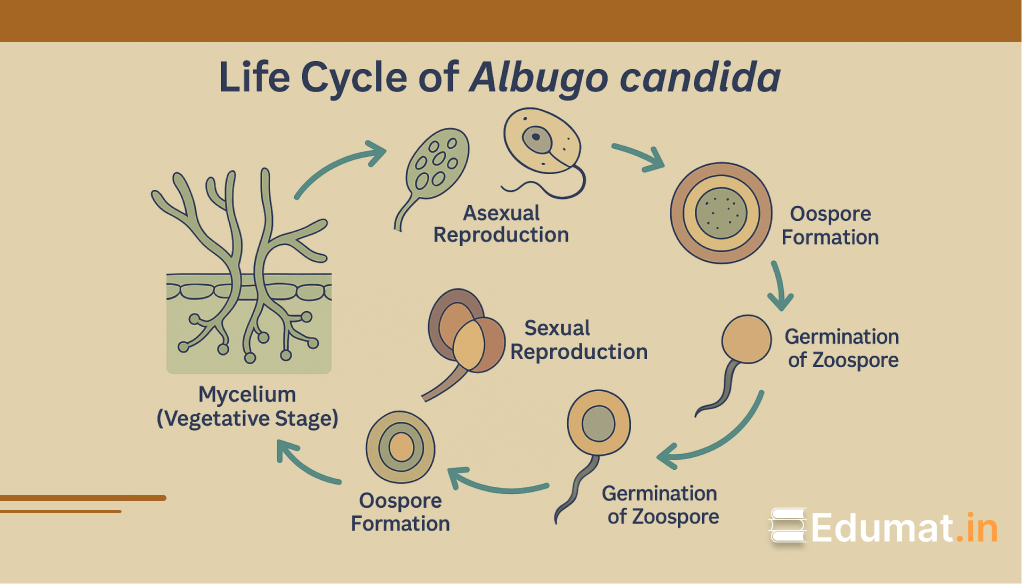
1️⃣ Mycelium (Vegetative Stage)
The mycelium of Albugo candida is:
- Aseptate, coenocytic (multinucleate), and intercellular.
- Grows vigorously inside host tissue.
- Forms haustoria to absorb nutrients from host cells.
2️⃣ Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction occurs through zoosporangia:
- Zoosporangia are produced in chains beneath the host epidermis.
- These burst out, releasing biflagellate zoospores.
⚛️ Zoospore Characteristics:
- Shape: Reniform (kidney-shaped), uninucleate.
- Flagella:
- Tinsel-type (anterior).
- Whiplash-type (posterior).
🧬 Germination of Zoospore:
- Flagella are withdrawn, and zoospore encysts.
- Encysted zoospore germinates → produces a germ tube.
- Germ tube enters host via stomata → new primary infection.
3️⃣ Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves specialized gametangia:
🧫 (a) Oogonium (Female Gametangium):
- Forms at the tip/intercalary part of a female hypha.
- Initially multinucleate and vacuolated.
- Differentiates into:
- Ooplasm: Central, dense, lipid-rich → becomes egg.
- Periplasm: Outer layer, vacuolated, rich in nuclei and organelles.
- 👉 Through mitosis, only one nucleus remains in ooplasm → female gamete.
🧬 (b) Antheridium (Male Gametangium):
- Develops at the tip of a male hypha.
- Initially multinucleate, but only one functional nucleus.
- Paragynous → attaches to the side of oogonium.
💞 (c) Fertilization:
- Fertilization tube grows from antheridium → enters oogonium → reaches ooplasm.
- Male nucleus fuses with female nucleus → forms zygote.
4️⃣ Oospore Formation
The zygote develops into an oospore:
- Resting, thick-walled, 5-layered structure.
- Contains reserve nutrients for long dormancy.
- Surrounded by persistent periplasm and oogonial wall.
5️⃣ Meiosis (Zygotic)
The location of meiosis is debated:
- Walker (1969): Meiosis occurs in oospore → zygotic meiosis.
- Sansome & Sansome (1974): Meiosis occurs in gametangia → gametangial meiosis.
- 👉 Most accepted view: Zygotic meiosis → haploid life cycle.
6️⃣ Germination of Oospore
Under favorable conditions (10–20°C):
- Oospore wall cracks → forms a germ tube or zoospore vesicle.
- Produces biflagellate zoospores.
- Zoospores initiate primary infection → life cycle repeats.
📚 Summary
The life cycle of Albugo candida can be summarized as:
✍️ Conclusion
The life cycle of Albugo candida demonstrates a fascinating balance between:
- Rapid asexual multiplication through zoospores.
- Sexual reproduction ensuring genetic variation and survival through resistant oospores.
Understanding its life cycle helps us tackle diseases like white rust in important crops such as mustard, cabbage, and other cruciferous vegetables.
📚 Want to Learn More About Plant Pathology?
Get smart notes, tutorials, and resources in slide & PPT format — all in one place.
👉 Boost your biology knowledge on Edumat.in – your science learning hub!
🔖 Tags
Albugo candida life cycle mycelium zygotic meiosis asexual reproduction sexual reproduction white rust