Photosynthesis in Plants: Process, Significance, and Mechanism
Science • June 7, 2025
Swaraj Barik
Introduction
Photosynthesis is the fundamental biological process through which green plants capture solar energy and convert it into chemical energy. This process sustains life on Earth by producing oxygen and organic food.
📌 The term photosynthesis literally means "synthesis using light."
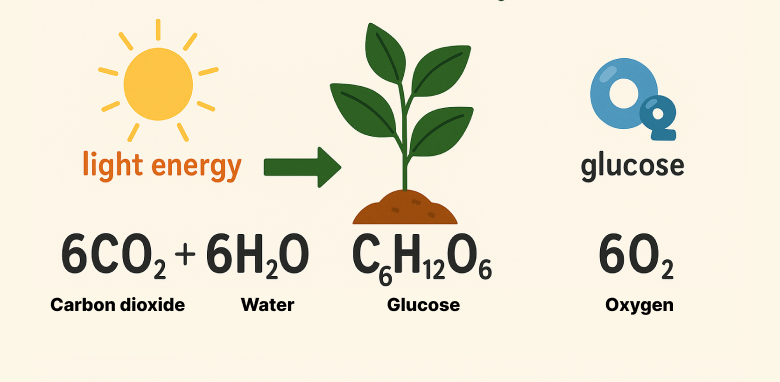
In this process, solar energy is used to combine carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) into glucose, releasing oxygen (O₂) as a byproduct.
👉 It is an anabolic and endergonic reaction—meaning it builds complex molecules and requires energy input.
🧪 Overall Equation of Photosynthesis
Simplified general equation:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Van Neil and Robert Hill demonstrated that the oxygen released comes from water, not carbon dioxide.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Here’s why photosynthesis is crucial for life on Earth:
- 🌱 Life-Sustaining Process: Primary source of food and energy for all living organisms.
- 🌿 Autotrophy: Green plants produce organic compounds from inorganic substances.
- 🔗 Producer-Consumer Chain: All heterotrophs depend on autotrophs (green plants) for nourishment.
- ⚡ Energy Storage: Converts solar energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
- 🛢️ Fossil Fuels Origin: Coal, petroleum, and gas originated from plant materials formed via photosynthesis.
- 🌳 Useful Plant Products: Timber, rubber, oils, fibers, and medicinal compounds.
- 🌬️ Oxygen Release: Maintains atmospheric oxygen, crucial for respiration and ozone layer formation.
- 🌎 Carbon Dioxide Reduction: Helps regulate CO₂ levels, minimizing its harmful effects.
- 🌾 Agricultural Productivity: Crop yield directly correlates with photosynthetic efficiency.
Magnitude of Photosynthesis
👉 Only 0.2% of sunlight reaching Earth is used in photosynthesis.
✅ Annually:
- 70–80 billion tonnes of CO₂ are fixed.
- About 1,700 million tonnes of dry organic matter is produced.
- 🌊 Oceans account for approximately 90% of this activity.
Light and Dark Reactions
Photosynthesis consists of two interconnected phases:
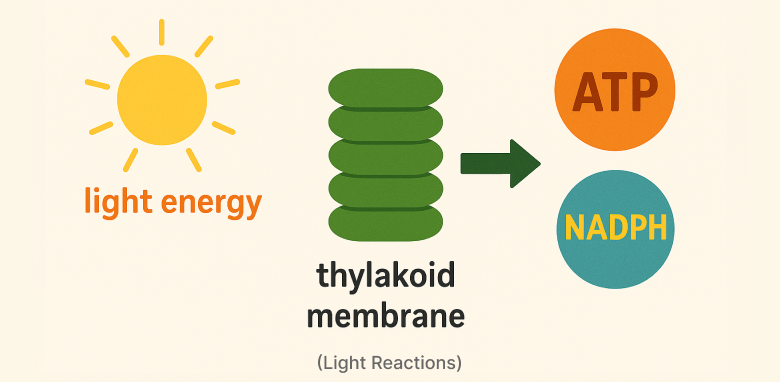
1. Light Reactions
Occur in thylakoid membranes. Convert light energy into ATP and NADPH.
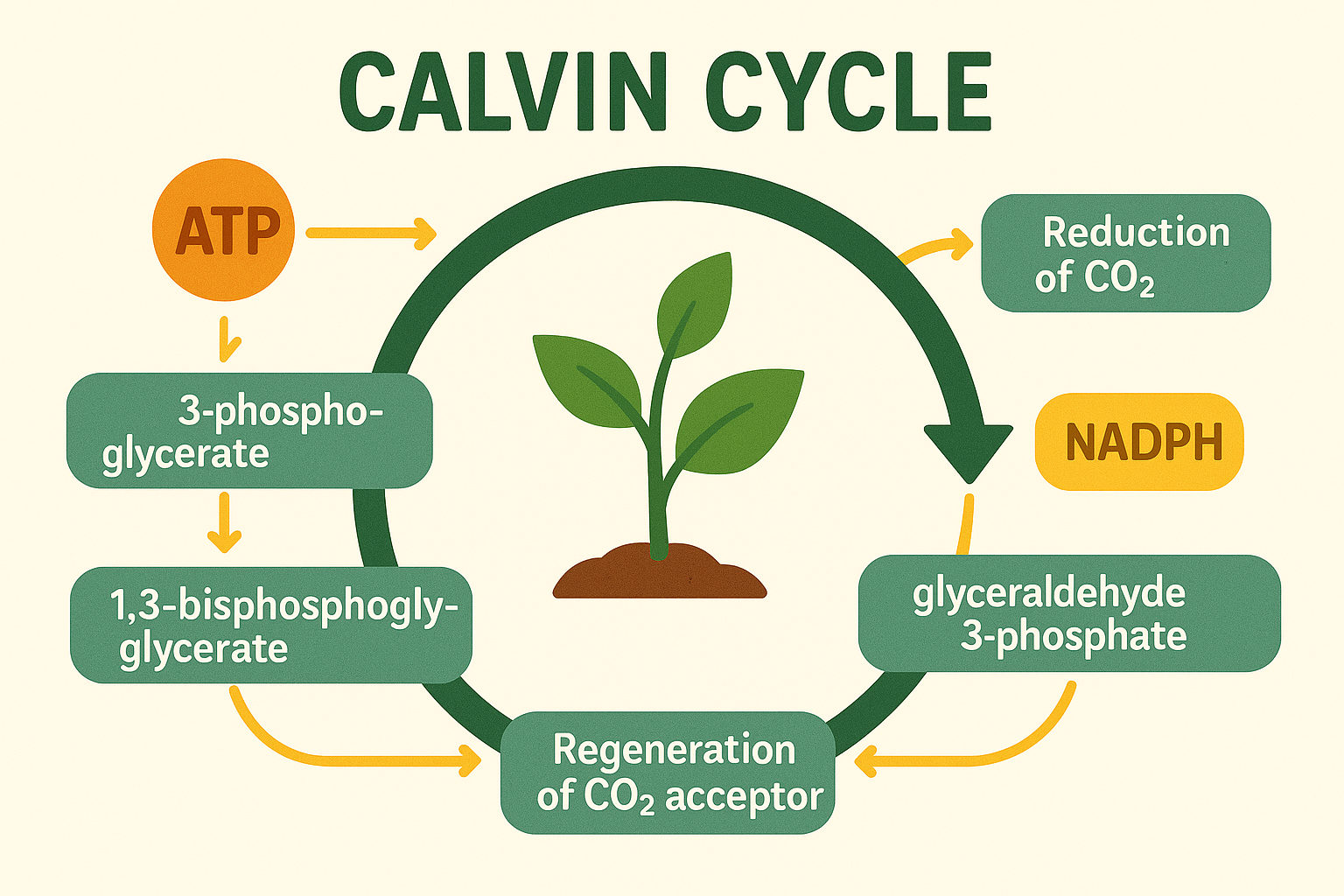
2. Dark Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
Occur in the stroma. Use ATP and NADPH to fix CO₂ into glucose.
➡️ Light reactions provide the energy required by dark reactions.
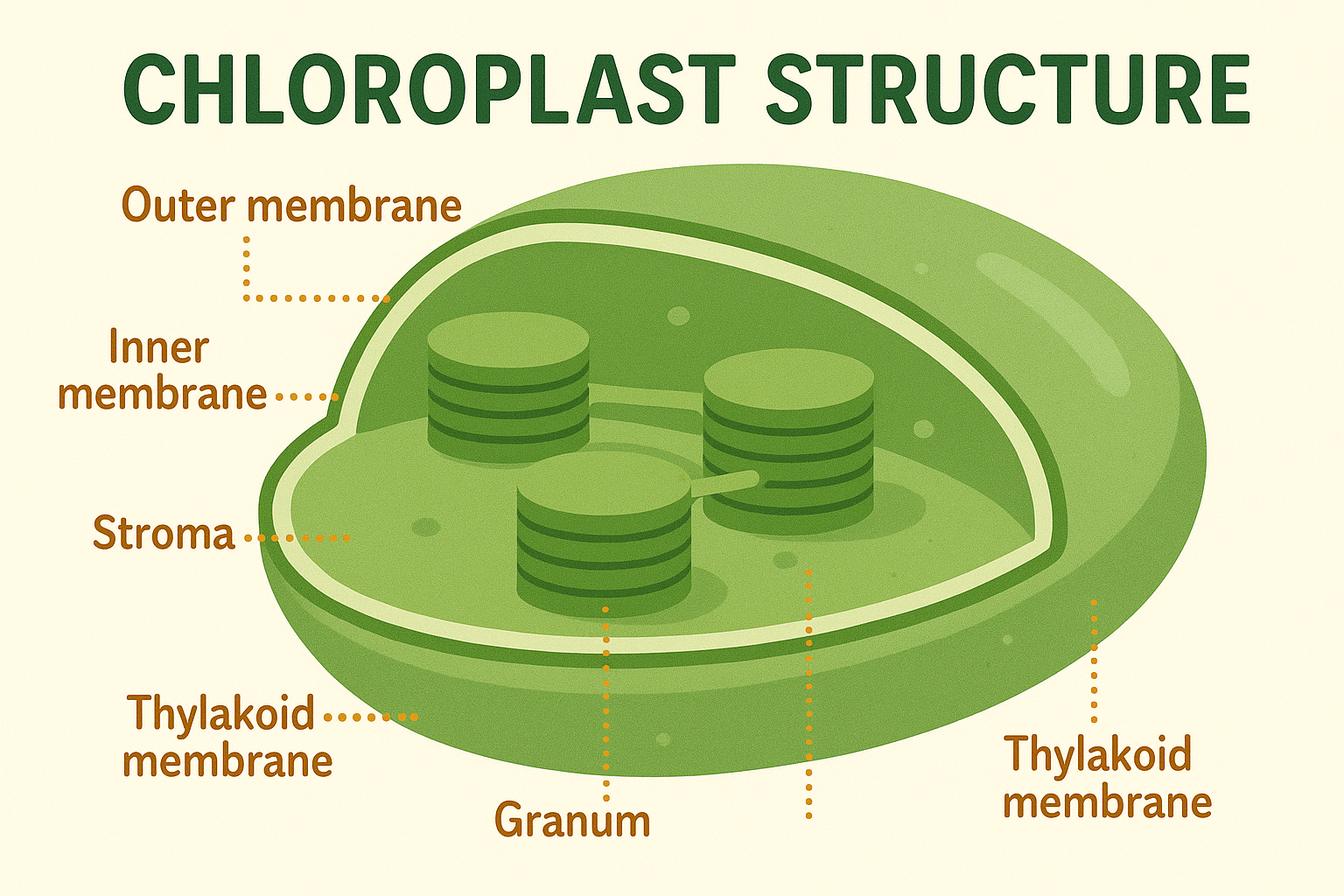
Site of Photosynthesis: The Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are double-membraned organelles found in green plant cells.
📍 Structure:
- Stroma: Fluid matrix with enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, starch grains, and trace minerals.
- Thylakoids: Flattened sacs containing photosynthetic pigments; organized into stacks called grana.
- Stroma Lamellae: Connect grana and support thylakoid structure.
💡 In prokaryotes (cyanobacteria and photosynthetic bacteria), photosynthesis occurs in specialized membranes (since they lack chloroplasts).
Photosynthetic Mechanism
Photosynthesis is a redox process:
Light Reaction
- ✅ Occurs in thylakoids.
- ✅ Generates ATP and NADPH.
- ✅ Releases oxygen from water (oxygenic photosynthesis).
Dark Reaction
- ✅ Occurs in the stroma.
- ✅ Fixes CO₂ into glucose using ATP and NADPH.
👉 Some bacteria perform anoxygenic photosynthesis (using other donors—not water—and do not release oxygen).
Photosynthetic Pigments
1️⃣ Chlorophylls
Primary green pigments (Chlorophyll a & b). Chlorophyll a is universal and essential.
Structure: Porphyrin ring (with central Mg) + phytol tail.
2️⃣ Carotenoids
Yellow, orange, or red pigments.
Types:
- Carotenes (e.g., β-carotene).
- Xanthophylls (e.g., lutein).
- 👉 Precursors of Vitamin A.
3️⃣ Phycobilins
Water-soluble pigments in algae.
Types:
- Phycoerythrin (red).
- Phycocyanin (blue).
Nature of Light
Light is composed of photons, each carrying energy (quantum).
👉 Energy is inversely related to wavelength.
📏 Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR):
- Range: 300–780 nm.
- Maximum absorption: Red and blue regions of the visible spectrum.
Leaf Interaction with Light
Leaves interact with light as follows:
| Interaction | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Absorbs | ~83% |
| Reflects | ~12% |
| Transmits | ~5% |
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is not just a plant process; it is the foundation of life on Earth. 🌍 It provides:
- ✅ Oxygen
- ✅ Food
- ✅ Fuel
- ✅ Atmospheric balance
Understanding its mechanism helps us:
- Improve crop productivity
- Address environmental challenges
- Combat climate change
🌱 Final Thought: Without photosynthesis, there would be no life as we know it. 🌞 It is the process that connects the Sun to the biosphere—a miracle of nature worth understanding and protecting.
📚 Want to Learn More About Biology?
Get smart notes, tutorials, and resources in slide & PPT format — all in one place.
👉 Boost your biology knowledge on Edumat.in – your science learning hub!
🔖 Tags
photosynthesis plant biology light reactions Calvin cycle chloroplasts photosynthetic pigments